Water Can Change State Over and Over Again
What Is the H2o Cycle?
The Short Answer:
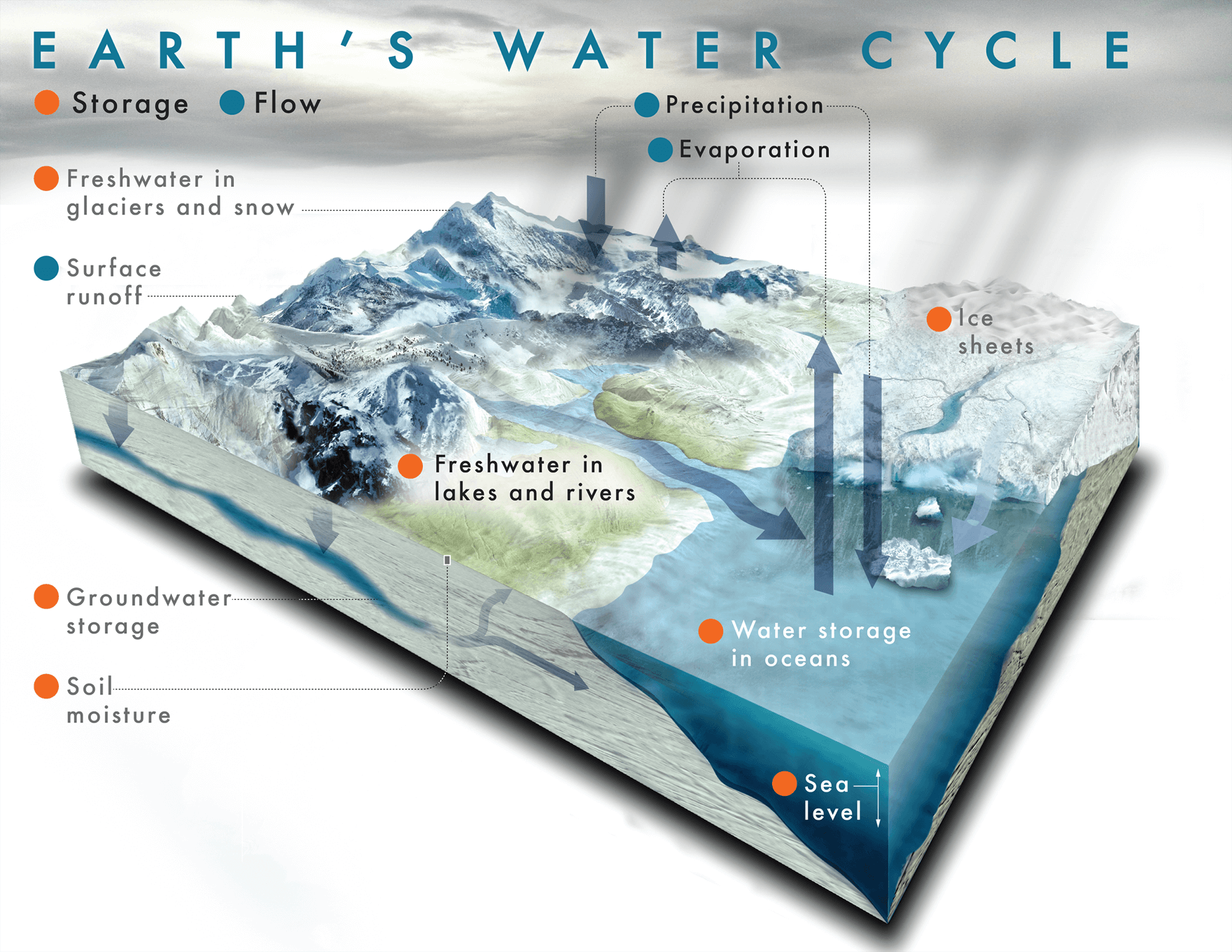
The water cycle is the path that all water follows as it moves effectually Earth in different states. Liquid h2o is found in oceans, rivers, lakes—and even cloak-and-dagger. Solid ice is found in glaciers, snowfall, and at the North and South Poles. Water vapor—a gas—is constitute in Earth's atmosphere.
Water can exist found all over Earth in the ocean, on state and in the atmosphere. The water bicycle is the path that all water follows as information technology moves around our planet.
On Earth, you can find water in all 3 states of matter: solid, liquid and gas. Liquid h2o is constitute in World's oceans, rivers, lakes, streams—and even in the soil and underground. Solid ice is found in glaciers, snow, and at the Northward and South Poles. Water vapor—a gas—is found in Earth's atmosphere.
How does water travel from a glacier to the ocean to a deject? That's where the water cycle comes in.
The H2o Cycle
Credit: NASA/JPL-Caltech
The Sunday'southward heat causes glaciers and snow to melt into liquid water. This h2o goes into oceans, lakes and streams. H2o from melting snow and ice also goes into the soil. There, it supplies h2o for plants and the groundwater that nosotros drink.
Snowfall falling on a glacier during wintertime months usually replaces whatsoever h2o that melts away in the summertime. However, due to Globe's overall warming, most glaciers today are losing more ice than they regain, causing them to shrink over time.
How does water get into the atmosphere? At that place are two main ways this happens:
- Rut from the Sun causes h2o to evaporate from oceans, lakes and streams. Evaporation occurs when liquid water on Earth'southward surface turns into water vapor in our temper.
- Water from plants and trees besides enters the atmosphere. This is chosen transpiration.
Warm water vapor rises upward through Earth'southward atmosphere. As the h2o vapor rises higher and higher, the cool air of the atmosphere causes the water vapor to turn dorsum into liquid water, creating clouds. This procedure is called condensation.
When a cloud becomes full of liquid water, it falls from the sky every bit rain or snowfall—too known as precipitation. Rain and snow so make full lakes and streams, and the process starts all over again.
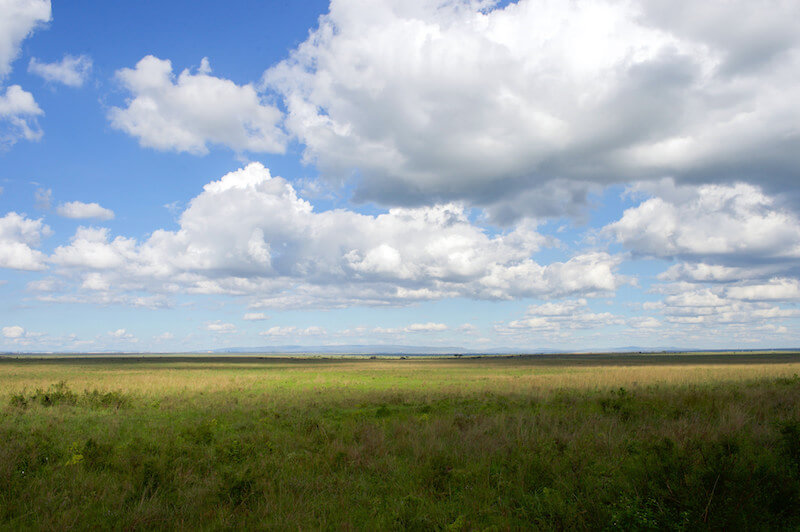

Clouds, like these over the savannah in Nairobi, Kenya, form when water vapor in the temper condenses back into liquid water. Credit: Department of Land
Why Do We Care About the Water Cycle?
We care about the water bike because water is necessary for all living things. NASA satellites orbiting Earth right now are helping usa to understand what is happening with water on our planet.

Water in the Soil
Humans need water to drink, and to water the plants that grow our food. NASA has a satellite called SMAP—brusk for Soil Moisture Active Passive—that measures how much water is in the acme 2 inches (five cm) of Earth'southward soil. This tin help us sympathize the relationship between water in the soil and astringent weather conditions, such as droughts.

Water in the Atmosphere
NASA's CloudSat mission studies water in our atmosphere in the form of clouds. CloudSat gathers information about clouds and how they play a function in World's climate. Also, the international satellite called the Global Precipitation Measurement Mission (GPM) observes when, where and how much it rains and snows on Globe.

Water in the Oceans
As Earth's climate becomes warmer, land ice at the Northward and South Poles starts melting. The water then flows into the body of water, causing sea level to ascent. NASA's Jason-3 mission—brusk for Joint Altimetry Satellite Oceanography Network-3—orbits Earth collecting data most ocean level and ocean temperature. This helps track how the ocean responds to Earth's changing climate.
NASA is also tracking how Earth'due south water moves all around our planet. This is the work of the GRACE-FO—or Gravity Recovery and Climate Experiment-Follow On—mission. It tracks the motility of water from one month to the next, and can even mensurate changes in deep groundwater hundreds of anxiety below Earth's surface.
NASA's Aqua satellite besides collects a large amount of information about Earth'due south water cycle, including water in the oceans, clouds, ocean ice, land ice and snow cover.
Related NASA Missions

Aqua

CloudSat

GPM
GRACE-FO
Jason-three

SMAP
Source: https://climatekids.nasa.gov/water-cycle/
Post a Comment for "Water Can Change State Over and Over Again"